Hydroponic Leaves Drooping
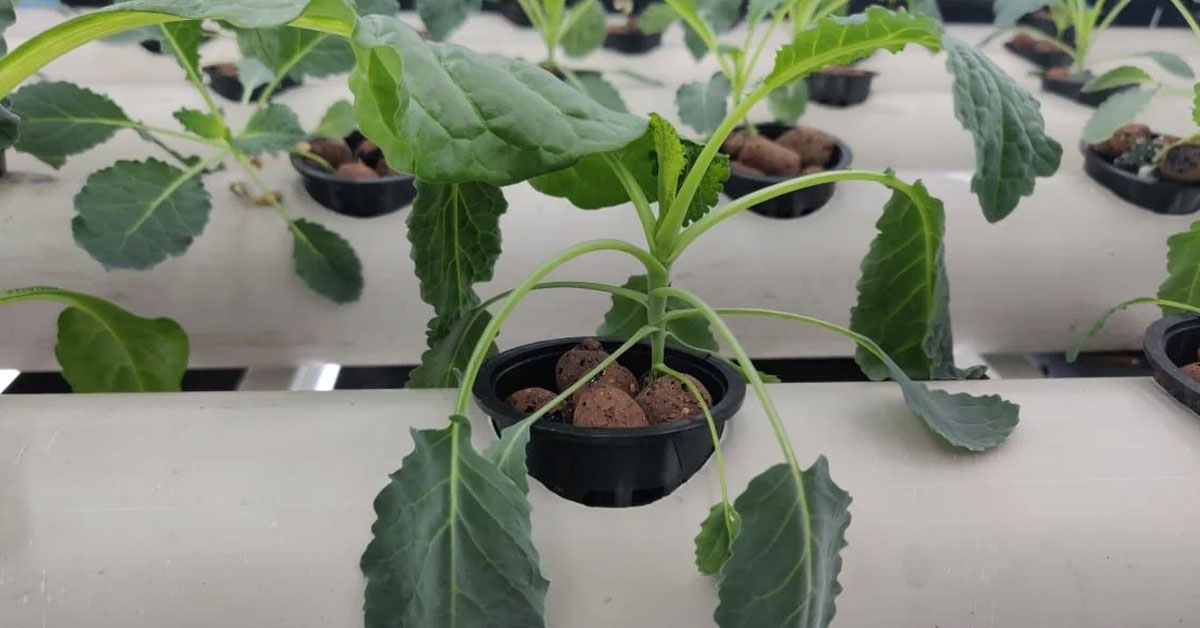
Hydroponic gardening, the practice of growing plants without soil, is an innovative method that allows plants to be grown indoors, year-round.
However, one common challenge faced by many hydroponic gardeners is the occurrence of the “hydroponic leaves drooping” phenomenon.
This term refers to a condition where leaves wilt or droop and is often a sign of distress in the plant.
Throughout this document, we will explore the causes and solutions for hydroponic leaves drooping, providing useful tips on how you can maintain a thriving hydroponic garden.
To begin, let’s explore the causes of hydroponic leaves drooping. The most common cause is nutrient deficiency, which occurs when there are insufficient nutrients in the water or grow medium that your plants are sitting in.
This can be resolved by adding more nutrients or fertilizer to your solution. Another possible cause could be a lack of light for photosynthesis
Identify the cause of your hydroponic leaves drooping
One common cause of drooping leaves in a hydroponic system is inadequate water or nutrient absorption.
This can occur if the roots are not receiving sufficient oxygen, which is essential for them to absorb the nutrients from the water.
Alternatively, overwatering can also lead to drooping leaves. It’s a delicate balance—too little or too much water can cause your plants to suffer.
Additionally, fluctuations in temperature, improper pH levels, and pest infections can also lead to drooping leaves.
Hence, regular checks on your system, water quality, and careful monitoring of the plant’s health can help prevent this issue.
Assess the environment around your hydroponic plants to determine changes that need to be made
To successfully assess your hydroponic environment, you need to pay attention to key factors such as light, temperature, and humidity.
Light
Hydroponic plants require adequate light for photosynthesis. Check if your plants are receiving the right amount of light—too much can cause them to wilt, while too little can stunt their growth. Consider adjusting the placement of your grow lights or the duration they’re turned on.
Temperature
Hydroponic plants thrive at temperatures between 68 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit. If the temperature in your growing area is outside this range, you may need to implement changes like installing a heating or cooling system.
Humidity
The ideal humidity level for hydroponic plants is between 40 and 60 percent. Too low humidity can lead to dehydration, whereas too high can result in fungus or disease. Use a humidity gauge to monitor levels and adjust as needed.
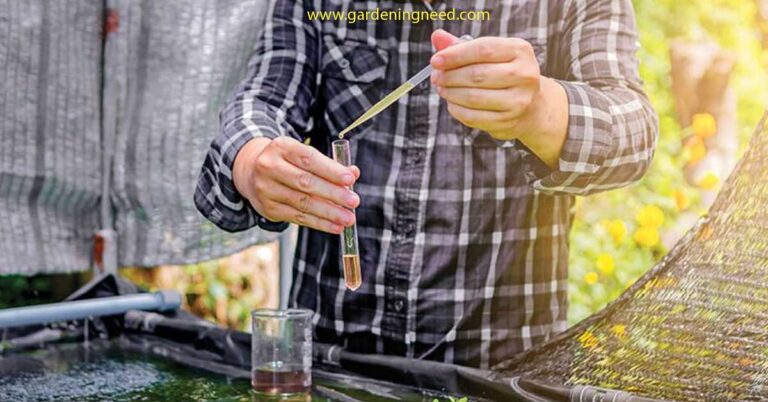
Consider adjusting the pH balance of the water for optimal growth
The pH level of your hydroponic water plays a critical role in nutrient absorption, directly impacting plant growth.
Hydroponic plants typically thrive in a slightly acidic environment with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. Too high or too low pH levels can prevent nutrient absorption, leading to nutrient deficiencies and subsequently drooping leaves.
Regularly testing the pH level of your water and adjusting it using pH buffers is necessary to ensure that your plants can effectively absorb nutrients and maintain healthy growth.
Check for signs of pests or diseases on the leaves and treat accordingly
Pest infestations and diseases can significantly contribute to drooping leaves in hydroponic systems.
To identify these issues, carefully inspect the leaves, stems, and roots of your plants for signs like spots, discoloration, or unusual growth patterns.
Pests such as aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies may be visible to the naked eye, but other diseases like root rot or fungal infections might require closer examination.
For pest control, consider introducing natural predators, using organic insecticides, or manually removing the pests if the infestation is manageable.
Remember, early detection and treatment are key to effectively managing pests and diseases.
In the case of fungal infections or diseases, it might be necessary to remove and isolate infected plants to prevent the spread to healthy ones.
Utilizing fungicides or adjusting environmental factors, like humidity and temperature, can also help in treating these conditions.
Always be sure to clean your hydroponic system regularly and thoroughly to minimize the risk of disease and pest infestations.
Provide proper nutrients to satisfy the plant’s needs
Supplying the correct balance of nutrients is vital to the health and productivity of your hydroponic plants.
Unlike soil-grown plants, hydroponic plants rely entirely on nutrient solutions for their nutritional requirements.
These solutions should provide all the essential macronutrients – nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur – and micronutrients – iron, manganese, boron, molybdenum, zinc, and copper – that plants need for growth.
The concentration of these nutrients in your solution should be carefully calibrated to your specific plants’ needs.
Over-concentration can lead to nutrient burn, while under-concentration can result in nutrient deficiencies, both of which can cause leaf drooping.
Regular testing of your nutrient solution using a nutrient meter can help ensure that your plants are receiving the right balance.
Remember to also refresh your nutrient solution regularly to maintain nutrient availability and prevent the buildup of salts that can harm plant roots.
Furthermore, consider using high-quality, hydroponic-specific nutrient solutions, which are designed to be easily absorbed by plants in water-based growing environments.
By providing the right nutrients in the right amounts, you can boost your hydroponic plants’ health and productivity, preventing issues like drooping leaves.
Investigate if there is proper light exposure and adjust accordingly
In a hydroponic system, ensuring proper light exposure is paramount for plant growth and overall health.
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy for growth, is directly influenced by the amount and quality of light plants receive.
Check the intensity and duration of light exposure in your hydroponic system. If plants are receiving too much intense light, they may show signs of wilting or burning. Conversely, inadequate light can lead to slow growth or weak, leggy plants.
Adjustments might involve moving your grow lights closer or further away from your plants, or tweaking the duration the lights are on each day.
For most plants, an exposure of 14-16 hours of light per day is optimal. However, it’s important to note that the specific needs can vary, depending on the plant species.
You may also need to consider the type of light; full-spectrum lights that mimic the sun’s natural rays are often the best choice for indoor hydroponic systems.
Lastly, remember to provide a period of darkness, as this is necessary for plant respiration and growth cycle.
Regularly monitoring light exposure and making necessary adjustments can help prevent problems such as drooping leaves and promote vigorous, healthy growth.
Conclusion
Hydroponic leaves drooping can be caused by a variety of factors – not enough nutrients, not enough light, over- or under-watering, etc.
Taking the time to assess and address any issues can help get your hydroponic plants back on track. Along with troubleshooting your existing vegetation, you may also want to consider adding on one last plant: hydroponic radishes.
When grown in water culture, hydroponic radishes are incredibly easy to grow and require very little maintenance.
Furthermore, they can produce a crop in as few as 30 days! Additionally, the diverse root system of this fast-growth root vegetable adds an interesting dynamic to any existing hydroponic garden.
So if you want to bring life back into your wilting foliage and create some flavorfully fresh foraging for friends and family, then why not consider experimenting with growing hydroponic radishes? Hopefully this brief overview helps give you more insight and motivation into exploring the possibilities of growing grassy greens underwater.