Build Hydroponics Grow Box: 4 Must-Know Tips for Success
The full potential of your gardening journey with a meticulously crafted hydroponics grow box. The art of cultivating your greens in a controlled environment, tailor made to enhance growth and yield. the seamless fusion of technology and nature as you embark on a sustainable and efficient gardening experience.
Elevate your harvest with a BUILD HYDROPONICS GROW BOX and witness the future of home cultivation.
How to Build Hydroponics Grow Box
Create Your Own Thriving Oasis
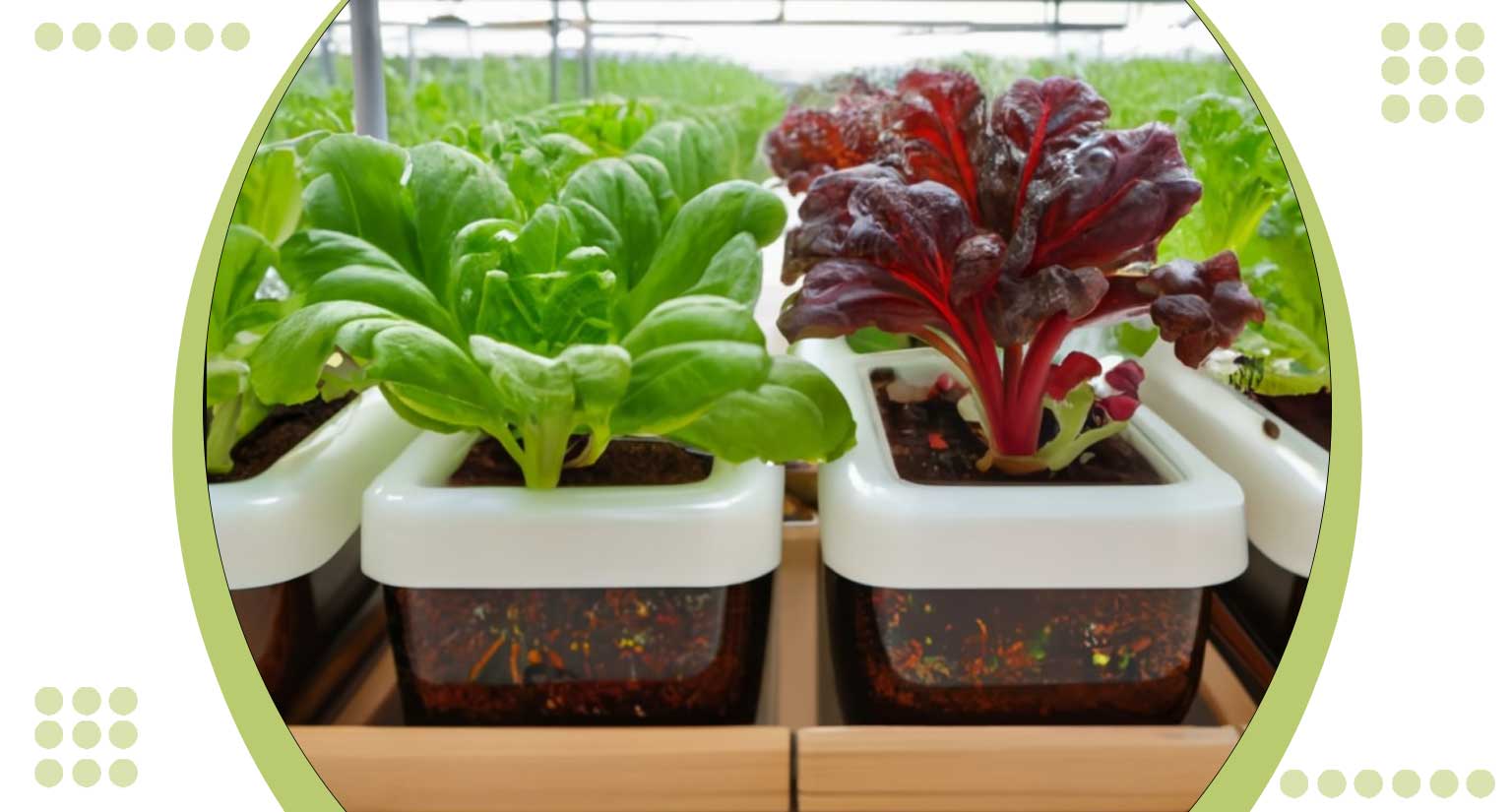
Building your hydroponics grow box is a rewarding endeavor that allows you to take control of your cultivation environment. Follow these comprehensive steps to craft your oasis of flourishing greens:
Materials and Tools
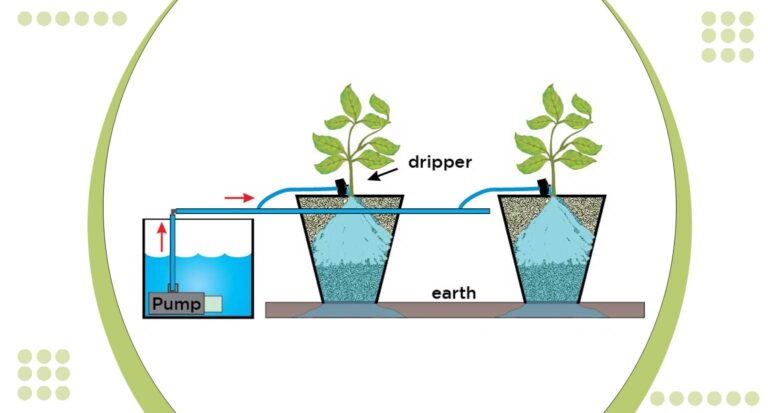
Gather essential materials like PVC pipes, connectors, grow lights, water pumps, a nutrient reservoir, and a durable container for your plants. Ensure you have tools such as a saw, drill, and measuring tape.
Design Your Box
Sketch the design of your grow box, keeping in mind the dimensions of your space. Plan for adequate space for the hydroponic system, lighting, and the number of plants you intend to grow.
Construct the Frame
Cut PVC pipes to your desired lengths and assemble the frame of the grow box. Secure the connections with PVC glue for added stability. This frame will serve as the backbone of your hydroponic setup.
Add Lighting
Install LED grow lights within the box to provide the essential spectrum for plant growth. Ensure the lights are adjustable to accommodate different plant heights and growth stages.
Integrate the Hydroponic System
Set up your chosen hydroponic system within the grow box. This can include nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), or other suitable methods. Connect the water pump to ensure proper nutrient circulation.
Include Ventilation
Incorporate a ventilation system with fans to maintain optimal air circulation. This helps prevent the buildup of heat and ensures a conducive environment for plant growth.
Monitor and Adjust
Install a reliable monitoring system to track pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and temperature. Regularly check and adjust these parameters to create an ideal environment for your plants.
Plant Your Seeds
Once your hydroponics grow box is set up, carefully plant your seeds or seedlings in the designated growing areas. Ensure they have access to the nutrient rich solution provided by the hydroponic system.
By following these steps, you’re on your way to cultivating a thriving hydroponic garden.
How much space do you need for hydroponics?
Tailoring Your Hydroponic Setup to Available Space
Determining the space needed for a hydroponic system involves considering the type of hydroponics, the number of plants, and the overall layout. Here’s a breakdown to help you customize your hydroponic space efficiently:
Indoor Hydroponics
For indoor hydroponic setups, allocate at least 2 square feet per plant. This includes the space needed for the plant, the hydroponic system, and any surrounding infrastructure like grow lights and ventilation.
Vertical Hydroponics
Utilize vertical space effectively by incorporating vertical hydroponic systems. These systems maximize the use of height, allowing you to grow more plants in a smaller footprint. Consider wall mounted or stacked systems for efficient vertical gardening.
Small Scale Systems
If space is limited, opt for compact hydroponic systems like nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC). These systems are suitable for tight spaces and can be set up on tabletops or shelving units.
Greenhouse Considerations
In a greenhouse setting, plan for sufficient space between hydroponic rows to allow for easy access, maintenance, and harvesting. Greenhouses provide flexibility, allowing you to scale your hydroponic operation based on available square footage.
Customization for Crop Types
Different crops may have varying space requirements. Tailor your hydroponic space based on the types of plants you intend to grow. Leafy greens, herbs, and smaller vegetables can be planted more closely, while larger plants may need additional space.
Walkways and Accessibility
Your hydroponic setup includes well designed walkways for easy access to all plants. This not only facilitates maintenance but also prevents overcrowding and shading between plants.
Scalability
Plan for scalability if you have the option to expand your hydroponic operation in the future. Leave room for additional systems or growing areas as your interest and expertise in hydroponics grow.
By considering these factors and customizing your hydroponic space based on your specific needs, you can make the most of the available area while ensuring optimal conditions for plant growth.
What are the 3 nutrients needed for hydroponic planting?
Fueling Growth with the Primary Nutrients
In hydroponic gardening, plants require a specific blend of nutrients to thrive without soil. The primary nutrients, often referred to as NPK, play a vital role in supporting various aspects of plant growth. Here are the three essential nutrients needed for hydroponic planting:
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is a fundamental component of amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis.
It plays a crucial role in promoting vigorous vegetative growth, ensuring healthy leaves, stems, and overall plant structure. In hydroponics, nitrogen is commonly supplied in the form of nitrate (NO3-) or ammonium (NH4+).
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is essential for energy transfer within the plant, facilitating processes such as photosynthesis and respiration.
It is particularly vital during the flowering and fruiting stages, promoting robust root development, flower formation, and seed production. Phosphorus is typically supplied in hydroponics as phosphate ions (H2PO4-).
Potassium (K)
Potassium is crucial for enzyme activation, osmoregulation, and the synthesis of carbohydrates. It plays a key role in enhancing plant tolerance to stress, disease resistance, and the overall quality of fruits and flowers.
In hydroponics, potassium is often supplied in the form of potassium nitrate (KNO3) or potassium sulfate (K2SO4).
These three nutrients, when provided in the correct ratios, form the foundation of a well balanced hydroponic nutrient solution.
In addition to these primary nutrients, plants also require secondary nutrients (calcium, magnesium, and sulfur) and micronutrients (iron, zinc, copper, manganese, molybdenum, and boron) in smaller quantities for optimal growth.
By understanding and carefully managing the nutrient composition of your hydroponic solution, you can create an environment that fosters healthy, productive plants.
Is hydroponic healthier than organic?
The comparison between hydroponic and organic gardening in terms of healthiness is nuanced, as both approaches have their own advantages and considerations. The key aspects of each method:
Hydroponic Gardening:
1. Nutrient Control
Hydroponics allows precise control over nutrient levels, pH, and environmental conditions.This can lead to faster plant growth and potentially increased yields.
2. Water Efficiency
Hydroponic systems are generally more water efficient compared to traditional soil based methods. The recirculation of nutrient solutions minimizes water wastage.
3. Reduced Pesticide Use
Since hydroponic systems are often soilless and controlled environments, there may be a reduced need for pesticides. Integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects, are commonly employed in hydroponics.
Organic Gardening:
1. Natural Inputs
Organic gardening relies on natural inputs, avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Instead, it focuses on compost, manure, and other organic amendments to nourish plants.
2. Soil Health
Organic gardening emphasizes soil health and biodiversity. Healthy soil is seen as the foundation for robust plant growth, and practices such as crop rotation and cover cropping are commonly employed.
3. Environmental Sustainability
Organic farming often prioritizes environmental sustainability, aiming to minimize the ecological impact of agriculture. This includes the avoidance of synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
The choice between hydroponic and organic gardening often depends on personal preferences, available resources, and specific goals.
Some individuals prefer the natural and traditional approach of organic gardening, while others appreciate the efficiency and controlled conditions offered by hydroponics.
Both methods can contribute to healthy and nutritious plant growth when implemented with care and attention to best practices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the BUILD HYDROPONICS GROW BOX opens the door to a revolution in home gardening, merging technology with nature. This innovative solution empowers enthusiasts to embark on a journey of efficient and year round cultivation.
With a meticulous focus on creating an optimal environment, this grow box promises a bounty of fresh produce.